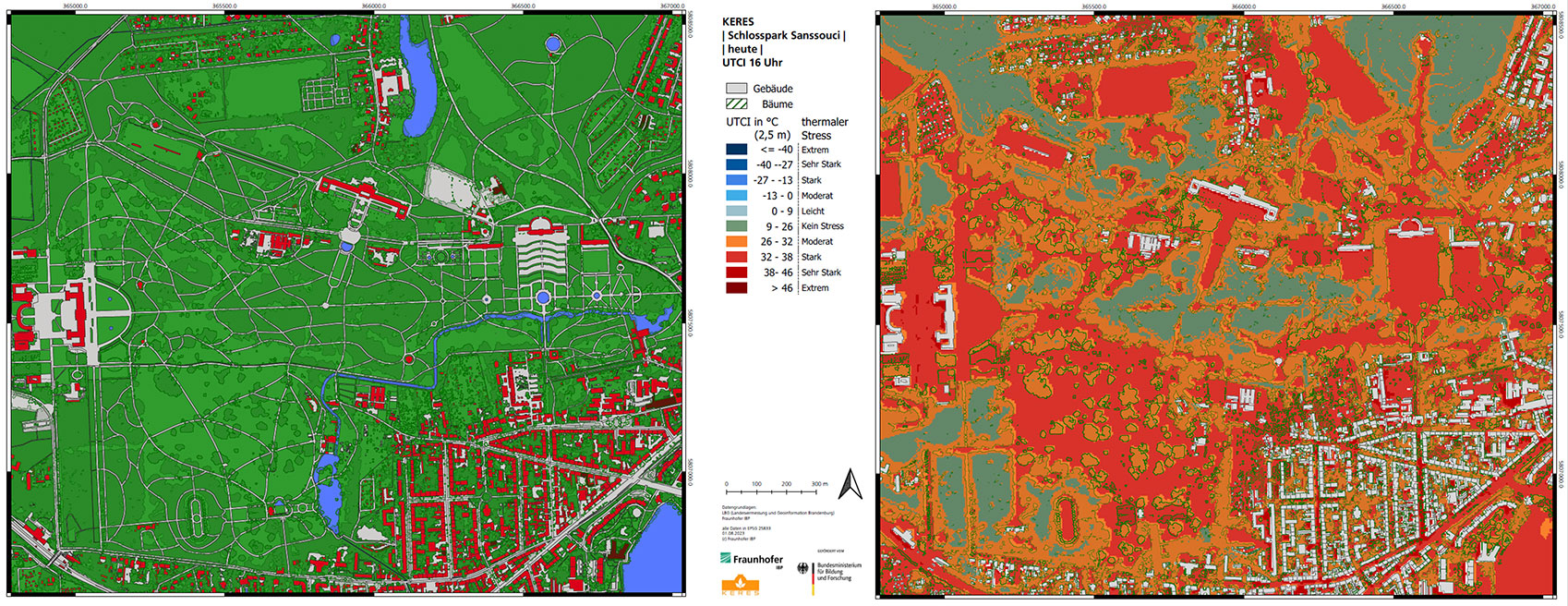
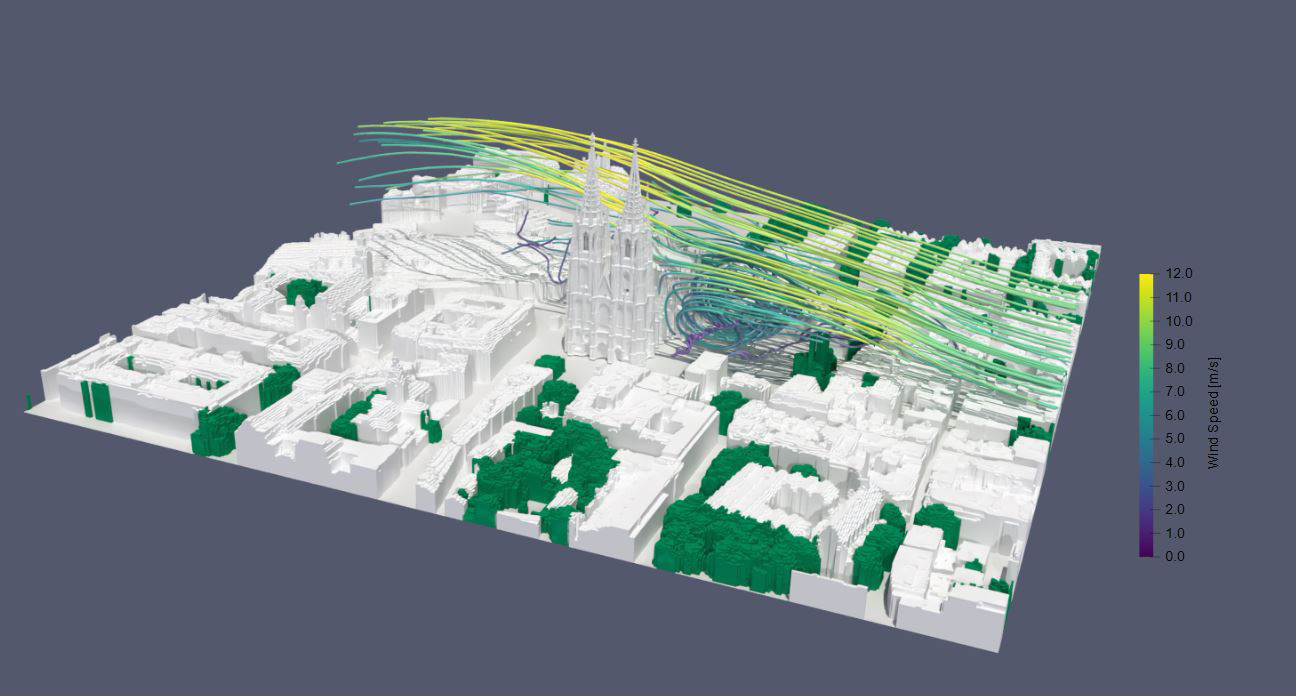
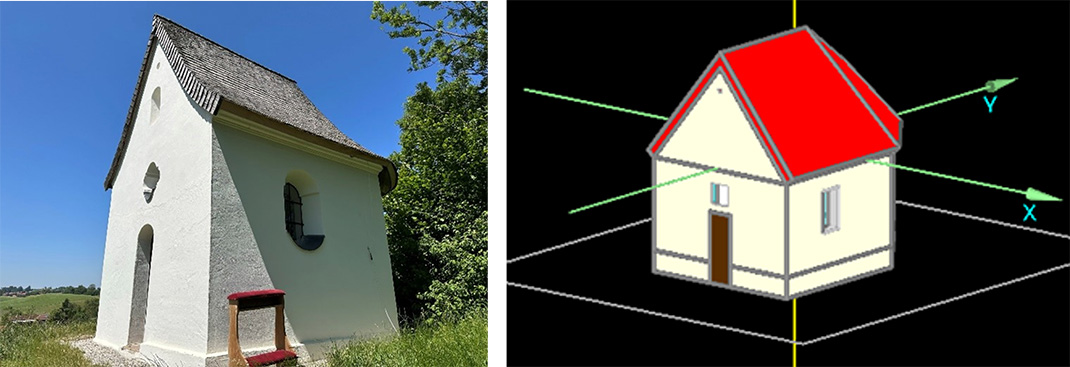
Predictions of the regional relevance of future extreme weather events and natural disasters were made for the five case studies in the project as a basis for assessing the risk of future damage to cultural heritage due to extreme weather events. They illustrate probable local changes in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events in the middle and at the end of the 21st century. At the same time, risk maps showing the effects of specific extreme weather events (heat loads in outdoor spaces and extreme wind events) were drawn up for selected case studies using hygrothermal building and urban climate simulations, thus substantiating the local risk for a property or object. In addition to this risk assessment, recommendations for preventive and protective measures were drafted: A catalog of measures for protecting and adapting typical regional construction methods and building types and for protecting and adapting historic gardens and parks was drawn up from each of the case studies. Furthermore, a façade protection system was developed specifically for half-timbered buildings. The KERES knowledge platform, which is based on a proprietary ontology, was developed to store and semantically link all relevant data.
Case study-related Climate Fact Sheets (CFS) were created as part of the project to provide a highly extensive and comprehensible overview. The fact sheets contain standardized information on future regional risks to cultural heritage from extreme weather events, taking possible uncertainties into account. Furthermore, a case study climate fact sheet (climate fact sheets for vulnerable historic buildings) was developed, containing additional information on location, history, materials, vulnerability and specific risks, organizational and structural measures already implemented and concepts for developing ways of adapting cultural heritage to future climate changes. In order to raise awareness of the risks posed by extreme weather events and to initiate prevention and adaptation processes, the Future Workshop concept was developed, in which measures and strategies for specific properties are devised together with stakeholders.